This article describes how to install and configure a terminal server role Remote Desktop Session Host in a workgroup (without an Active Directory domain) and without any other additional roles (Connection Broker, Remote Desktop Web Access, RDS Gateway). This will be a single server RDS deployment on Windows Server 2019/2022.
If you are going to use a separate RDS host in a workgroup, note that its functionality is limited. It cannot be scaled to a full-featured RDS farm, you cannot create separate collections or a RemoteApp, there is no Connection Broker, you cannot use User Profile Disks, there are no centralized management tools, RDS service won’t be available to users during maintenance operations if the host is in the drain mode.
How to Install Remote Desktop Services Role on Windows Server 2019/2022?
It is supposed that you have already installed Windows Server and configured basic settings (IP address, server name, time/date, installed updates, etc.). Then you can install the RDS role. To do it, you can use either Server Manager or PowerShell.
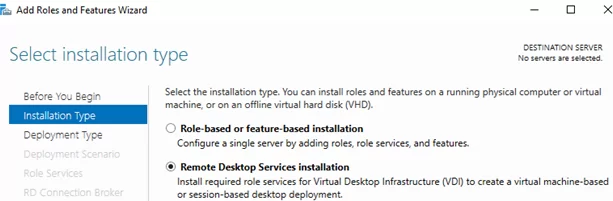
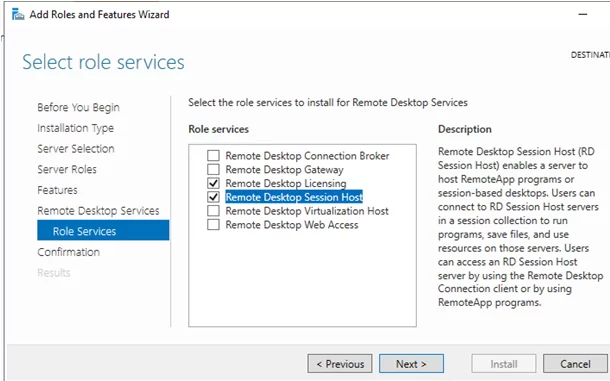
To install the RDS using Server Manager, select Remote Desktop Session Host and Remote Desktop Licensing in Role-based or Feature-based installation -> Server roles -> Remote Desktop Services in RDS components (agree to the installation of RSAT features to manage the roles).
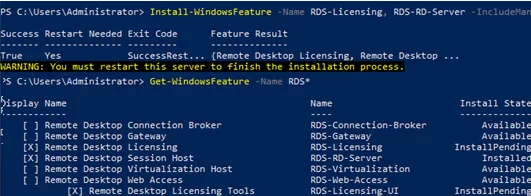
You can also install Windows Server roles using PowerShell:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name RDS-Licensing, RDS-RD-Server –IncludeManagementTools
Check which RDS roles are installed on your server:
Get-WindowsFeature -Name RDS* | Where installed
Restart your server:
Restart-Computer
Configure Remote Desktop Licensing Role and Add RDS Licenses (CALs)
The next step is to configure the Remote Desktop Licensing role, which provides licensing for user RDP connections. You can install and activate Remote Desktop Licensing on this host (if you have only one host in your network) or place the RDLicensing role on another server. One server with the RDS Licensing role can issue licenses to any number of RDS hosts.
If you have decided to use a local RDLicensing server, activate the RDS Licensing host and install client licenses (RDS CALs) following this guide.
Remote Desktop License Issue There is a problem with your Remote Desktop license, and your session will be disconnected in 60 minutes.
Configure Remote Desktop Session Host in a Workgroup
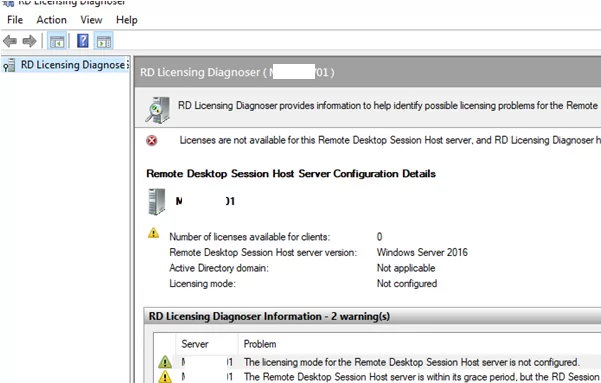
Go to Control Panel -> System and Security -> Administrative Tools -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Licensing Diagnoser. Note that your server is not yet configured to receive RDS CALs from the licensing server. The following messages prove it:
- The licensing mode for the Remote Desktop Session Host server is not configured
- Number of licenses available for clients: 0
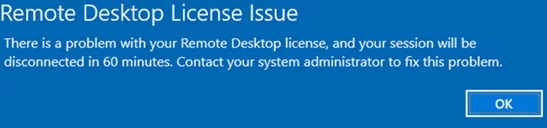
If you don’t target your RDSH server to the RDS licensing server able to issue CALs to your users, your server will stay in the trial mode. In this mode, RDS services work for 120 days only (at each connection, you will see this message in the tray: “The Remote Desktop service will stop working in xxx days”). After the grace period is over, users won’t be able to connect to RDS due to the following error:
The main disadvantage of Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 in a workgroup (without a domain), is that you don’t have any convenient administrative tools to manage the RDS role. You will have to configure any RDSH role settings in the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc).
Configure RDS licensing settings with the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc):
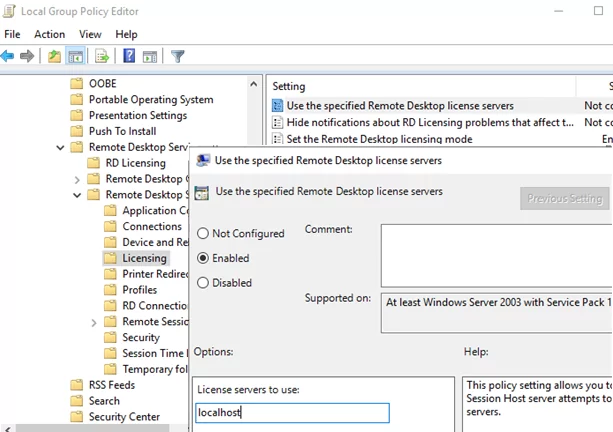
- Go to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Licensing;
- Change Set the Remote Desktop licensing mode to Per Device;
- In Use the specified Remote Desktop license servers option, specify the IP address of the server RDLicensing server is installed on. If the licensing server is installed locally, enter
localhostor127.0.0.1; - Update local Group Policy settings and run the Remote Desktop Licensing Diagnoser. Make sure that it sees your RDS CALs.
In the local GPO, you can also set RDP session limits (timeouts) and rules of disconnecting users when they are inactive.
Then create local user accounts on your RDS server. You can create users in lusrmgr.msc or with PowerShell:
$UserPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString "PaSS123!" -AsPlainText -Force
New-LocalUser a.brown -Password $UserPassword -FullName "Andi Brown"
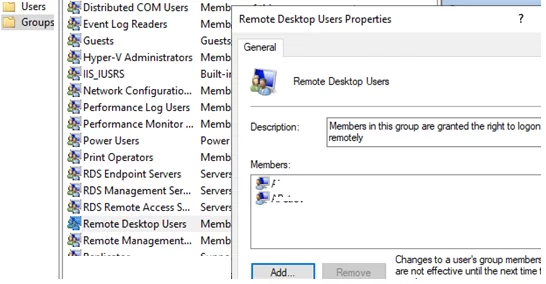
To allow a user to connect to a server through Remote Desktop Services, add the user account to the local Remote Desktop Users group. Add users manually using the computer management console or with PowerShell:
Add-LocalGroupMember -Group "Remote Desktop Users" -Member a.brown
Now users can try to connect to your RDS host using mstsc.exe (or any other RDS client) from their computers. Make sure that more than two active users can connect to the server simultaneously.
At the first login, a temporary license is issued for a user device (an RDS Per Device licensing feature). At the second logon, a permanent license is issued that appears in the Remote Desktop Licensing Manager. The license is issued for the period of 52-89 days (a random number).
If there are no free Per Device licenses, you can manually revoke licenses for some user devices. Use the RDSLicensing console or this PowerShell script:
$licensepacks = Get-WmiObject win32_tslicensekeypack | where {($_.keypacktype -ne 0) -and ($_.keypacktype -ne 4) -and ($_.keypacktype -ne 6)}
# the total number of per device licenses
$licensepacks.TotalLicenses
# the number of licenses issued to the devices
$TSLicensesAssigned = gwmi win32_tsissuedlicense | where {$_.licensestatus -eq 2}
# the computer name you want to revoke a license from
$compname="wksmun2a15"
$RevokePC = $TSLicensesAssigned | ? sIssuedToComputer -EQ $compname
$RevokePC.Revoke()
If you need to connect to a user RDP session, you can use the RDS shadow connection mode (it also works on an RDSH in a workgroup).
2 comments
You can convert User CALs to Device CALs in License Manager. Licensing Manager, right-click the license, Convert.
I have a Server Standard 2012 that i upgraded to 2019 and it works perfectly excpet for this part, I can not get the licensing service to start so the tools etc. still won’t work. What am I missing? I did all these steps. Is there something from 2012 interfering that I need to remove?