In this article, we’ll show you how to properly put an Exchange Server 2019/2016 host into maintenance mode. You must put your Database Availability Group (DAG) into maintenance mode if you are going to install updates on an Exchange Server host (Windows Updates or Exchange CU) or maintain your server hardware. When you enable maintenance mode, you must move active databases off the Exchange server and switch the queue to other servers.
The Exchange Server has two built-in PowerShell scripts for managing maintenance mode:
- StartDagServerMaintenance.ps1 – allows to move active databases and the Primary Active Manager (PAM) role to another server, and blocks the reverse migration of mailbox databases till the maintenance is over;
- StopDagServerMaintenance.ps1 – allows you to take the Exchange server out of maintenance mode by performing the reverse procedures.
These scripts are located in the Scripts folder (CD $ExScripts) of the Exchange installation directory. The following syntax is used:
.\StartDagServerMaintenance.ps1 -ServerName <ServerName> -MoveComment Maintenance -PauseClusterNode
.\StopDagServerMaintenance.ps1 -serverName <ServerName>
These scripts enable you to automate some operations. In most cases, Exchange administrators prefer to manually put the server into maintenance mode.
There is an example of a PowerShell script you can use to enable the maintenance mode for your Exchange server. Run the commands on a computer with the Exchange Management Shell and the RSAT-Clustering module installed:
Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.SnapIn
Import-Module FailoverClusters
Or you can connect to your Exchange Server remotely using PowerShell:
$Session = New-PSSession -ConfigurationName Microsoft.Exchange -ConnectionUri http://munexh01.woshub.com/PowerShell/ -Authentication Kerberos -Credential (Get-Credential)
Import-PSSession $Session
Set the names of your Exchange servers:
# a server that you want to enable the maintenance mode for
$maintance_srv = "munexh01.woshub.com"
# a target server you want to move mail queues to
$target_srv = "munexh02.woshub.com"
# Disable the HubTransport component of the server and put it into Draining mode
Set-ServerComponentState $maintance_srv –Component HubTransport –State Draining –Requester Maintenance
Restart-Service MSExchangeTransport
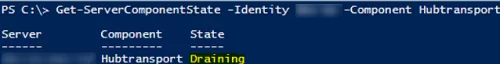
# Check that the HubTransport status has changed to Draining
Get-ServerComponentState -Identity $maintance_srv -Component Hubtransport
If you run Get-ServerComponentState -Identity $maintance_srv now, all Exchange components (except Monitoring and RecoveryActionsEnabled) will have the Inactive status.
# Move mail queue to another server
Redirect-Message -Server $maintance_srv -Target $target_srv
# Make sure that the mail queue have been cleared:
Get-Queue
# Pause your cluster node. This will move the Primary Active Manager (PAM) role to another DAG host
Suspend-ClusterNode –Name $maintance_srv
# Move all the mounted copies of mailbox databases to other servers
Set-MailboxServer $maintance_srv –DatabaseCopyActivationDisabledAndMoveNow $true
# Prevent a database activation on the server
Set-MailboxServer $maintance_srv –DatabaseCopyAutoActivationPolicy Blocked
Wait until the mailbox databases are successfully moved to another host (this will take a few minutes). Make sure that the list of mounted databases on the server is empty:
Get-MailboxDatabaseCopyStatus -Server $maintance_srv | where {$_.Status -like "Mounted"}
# Put Exchange components into maintenance mode
Set-ServerComponentState $maintance_srv –Component ServerWideOffline –State InActive –Requester Maintenance
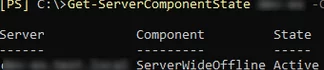
# Check if the server is in maintenance mode
Get-ServerComponentState -Identity $maintance_srv -Component ServerWideOffline
Get-MailboxDatabaseCopyStatus
Now you can complete the maintenance procedures for the Exchange host that you need. After you have done everything on the server, you need to perform the reverse steps to bring your Exchange Server host out of maintenance mode:
Set-ServerComponentState $maintance_srv –Component ServerWideOffline –State Active –Requester Maintenance
# You may check the status as shown below (it must change to Active):
Get-ServerComponentState $maintance_srv -Component ServerWideOffline
Resume-ClusterNode –Name $maintance_srv
Set-MailboxServer $maintance_srv –DatabaseCopyAutoActivationPolicy Unrestricted
Set-MailboxServer $maintance_srv –DatabaseCopyActivationDisabledAndMoveNow $false
Set-ServerComponentState $maintance_srv –Component HubTransport –State Active –Requester Maintenance
Check the Exchange Server status:
Test-ServiceHealth $maintance_srv
Rebalance your active mailbox databases across DAG hosts according to the configured activation preferences using RedistributeActiveDatabases.ps1:
cd $exscripts
.\RedistributeActiveDatabases.ps1 -DagName mun-dag –BalanceDbsByActivationPreference
Move-ActiveMailboxDatabase -Server $target_srv -ActivateOnServer $maintance_srv -Confirm:$false
Perform a MAPI availability check:
Test-MAPIConnectivity -Server $maintance_srv
Check database statuses and replication in the DAG:
Get-MailboxDatabaseCopyStatus
Test-ReplicationHealth -DatabaseAvailabilityGroup