How to manually kill a Windows service process that is stack at “Stopping” or “Starting” state? Most Windows administrators have faced a problem when they try to start/stop/restart a service, but it gets stuck with the Stopping (or Starting) status. You won’t be able to stop this service from the Service management console (services.msc), since all control buttons for this service become inactive (grayed out). The easiest way is to restart Windows, but it is not always acceptable. Let’s take a look at alternative ways, which allows to forcefully kill a stuck Windows service or process without system reboot.
If within 30 seconds after trying to stop the service, it doesn’t stop, Windows displays this message:
Windows Could not stop the xxxxxx service on Local Computer Error 1053: The service did not respond in a timely fashion.
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control /v ServicesPipeTimeout /t REG_SZ /d 600000 /f
This is useful when starting/stopping heavy services that do not have enough time to properly terminate all processes and close the files (for example, MS SQL Server).
If you try to stop such a service from the command prompt: net stop wuauserv, a message appears:
The service is starting or stopping. Please try again later.
or:
Windows could not stop the Service on Local Computer. [SC] ControlService Error 1061: The service cannot accept control messages at this time.
How to Force Kill a Stuck Windows Service Using TaskKill?
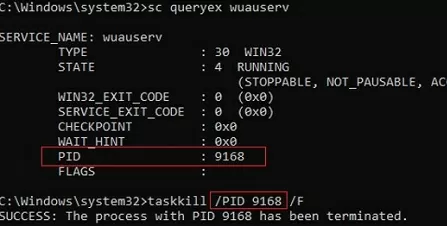
The easiest way to stop a stuck service is to use the built-in taskkill command-line tool. First of all, you need to find the PID (process identifier) of the service. As an example, let’s take the Windows Update service. Its system name is wuauserv (you can check the name in the service properties in the services.msc console).
Run this command in the elevated command prompt (it is important, or access denied error will appear):
sc queryex wuauserv
In our case, the PID of the wuauserv service is 9186.
To force kill a stuck process with the PID 9186, run the command:
taskkill /PID 9168 /F
SUCCESS: The process with PID 9168 has been terminated.
This command will forcibly terminate the service process. Now you can start the service with the sc start servicename command or through the service management console
You can stop a hung service more elegantly without manually checking the PID of the service process. The taskkill tool has the /FI option, which allows you to use a filter to select the necessary services or processes. You can kill a specific service with the command:
taskkill /F /FI "SERVICES eq wuauserv"
Or you can skip the service name at all and killing all services in a hung state with the command:
taskkill /F /FI "status eq not responding"
After that, the service that is stack in the Stopping status should stop.
You can also use the taskkill utility to force stop the hang services on a remote computer:
taskkill /S mun-fs01 /F /FI "SERVICES eq wuauserv"
Force Stop a Stuck Windows Service with PowerShell
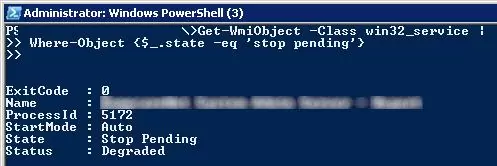
You can also use PowerShell to force the service to stop. Using the following command, you can get a list of services in the Stopping state:
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | Where-Object {$_.state -eq 'stop pending'}
Or in the Starting state:
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | Where-Object {$_.state -eq 'start pending'}
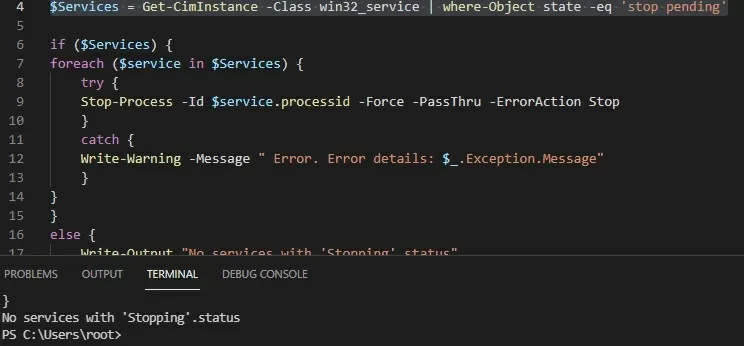
The Stop-Process cmdlet allows terminating the processes of all found services. The following PowerShell script will terminate all stuck service processes on Windows:
$Services = Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service -Filter "state = 'stop pending'"
if ($Services) {
foreach ($service in $Services) {
try {
Stop-Process -Id $service.processid -Force -PassThru -ErrorAction Stop
}
catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Error. Error details: $_.Exception.Message"
}
}
}
else {
Write-Output "No services with 'Stopping'.status"
}
Get-CimInstance instead of the Get-WmiObject cmdlet in the new PowerShell Core 6.x/7.x. Replace the first command of the script with:$Services = Get-CimInstance -Class win32_service | where-Object state -eq 'stop pending'
Analyzing the Wait Chains on Hung Services Using ResMon
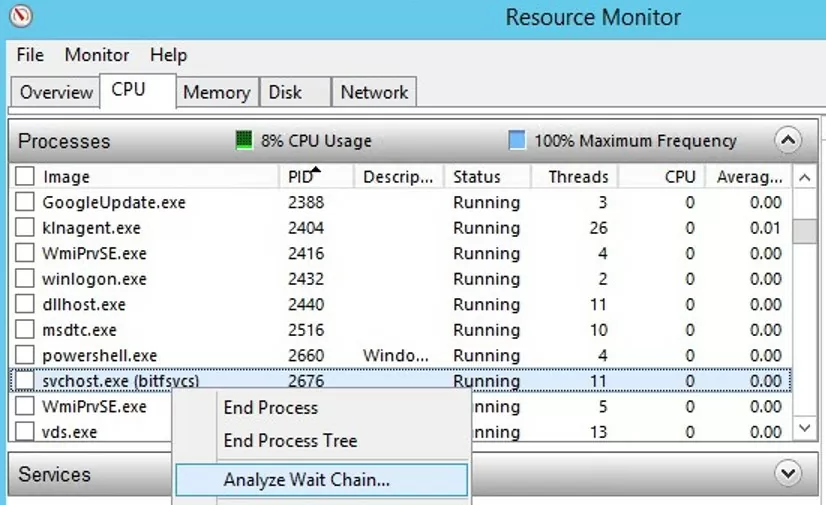
You can detect the process that caused the service to hang using the resmon.exe (Resource Monitor).
- In the Resource Monitor window, go to the CPU tab and find the hung service process;
- Select the item Analyze Wait Chain from the context menu;
- In the new window, you will most likely see that your process is waiting for another process. End the process. If you are waiting for the svchost.exe or another system process, you don’t need to terminate it. Try to analyze the wait chain for this process. Find the PID of the process that your svchost.exe is waiting for and kill it.
Killing a Hung Service Using Process Explorer
Even the local administrator cannot terminate some processes that run under the SYSTEM account. The fact is that the admin account simply hasn’t permissions on some processes or services. To stop such a process (service), you need to grant permissions to the service (process) to the local Administrators group and then kill them. To do this, we will need two small tools: psexec.exe and ProcessExplorer (available on the Microsoft website).
- To start the ProcessExplorer with the system privileges (runas SYSTEM), use the command:
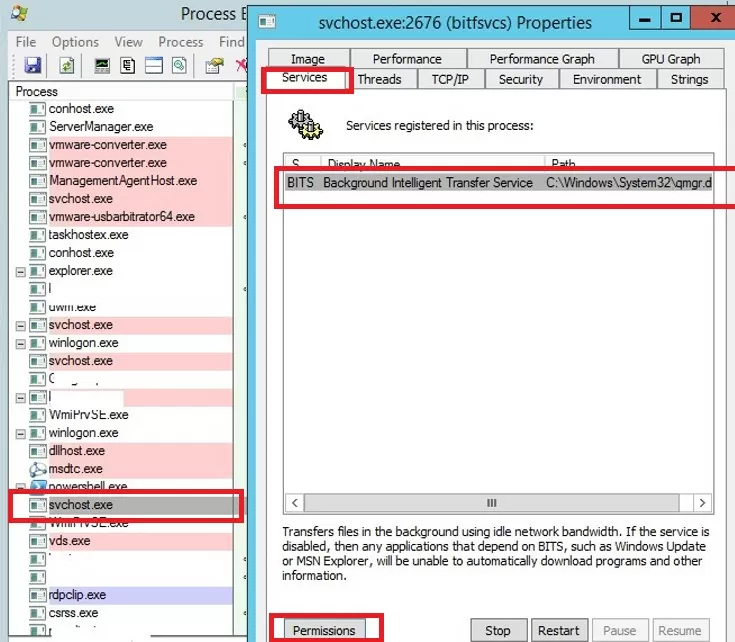
PSExec -s -i ProcExp.exe - In the Process Explorer process list, find the stuck service process and open its properties;
- Go to the Services tab, find your service and click the Permissions button;
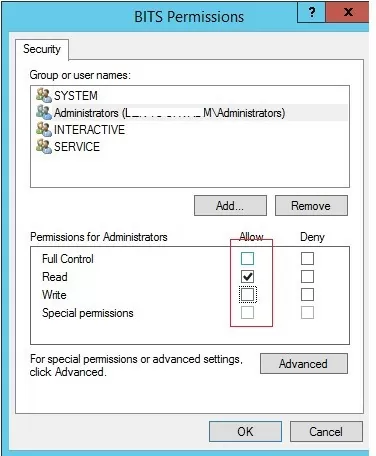
- Grant the Full Control right in the service permissions for the Administrators group. Save the changes;
- Now try to stop the service process.Please note, that the permission on the service is granted temporarily until it is restarted. To grant permanent permissions on service follow the article Set permissions on a Windows service.
5 comments
A product called System Frontier makes this super easy. When you view a list of services on a remote machine that are stuck in a “Start Pending” or “Stop Pending” state, you’ll have a button available to kill the service process. No need to look up the PID. It uses RBAC to determine if you’ve been granted the appropriate access to perform the action and there’s a full audit trail.
Terrific information very well laid out. Thank you.
Amazingly well written and “filter” taskkill alternative for automating the task and the Powershell script are a must! Thanks for sharing and documenting.
what about service with pid 0?
Deep insight yet concise. Rare to find for Windows. Please keep going