One of the useful PowerShell features is the opportunity to connect to databases on remote servers, including MySQL ones. Thus, you can address MySQL tables to access data directly from PowerShell console. In this article, we’ll deal with the examples of connection to MySQL DB from PowerShell script and some commands to read/write the data in database tables. To connect to a MySQL server, we need a special connector – MySQL .NET Connector, which can be downloaded from the official MySQL website.
By the time this article has been written, the latest available connector version was Connector/Net 6.9.9.
Download mysql-connector-net-6.9.9.msi and install MySQL .NET Connector in the minimal configuration.
In advance, create a database to work with on your MySQL server. All operations on the database server are performed from MySQL CLI command prompt, but you can use a graphic tool phpmyadmin or any other suitable utility.
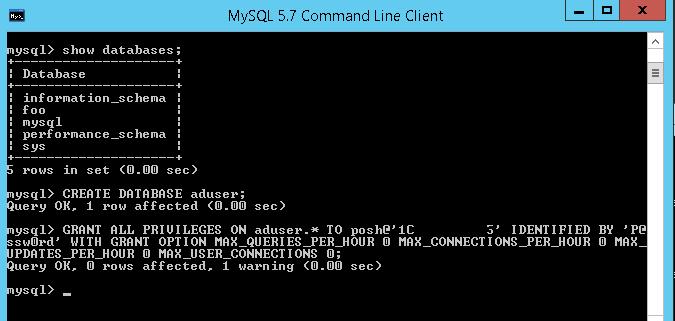
Create aduser database:
mysql> CREATE DATABASE aduser;
On your MySQL server, create a separate user with the privilege to connect to aduser database remotely. Grant this user the privilege to connect to the database remotely from the IP address 10.1.1.195:
mysql>GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON aduser.* TO posh@'10.1.1.195' IDENTIFIED BY 'P@ssw0rd' WITH GRANT OPTION MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_UPDATES_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_USER_CONNECTIONS 0;
Select the created database:
mysql> USE aduser;
And create the simplest table consisting from 3 columns: ID, AD username and e-mail address.
mysql> CREATE TABLE users (id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name VARCHAR(100), email VARCHAR(100), PRIMARY KEY (ID));
Go back to the server, from which we’ll connect to the MySQL database. Suppose, we want all names and e-mail addresses of the AD users to be shown in the table. You can get this information using Get-ADUser cmdlet.
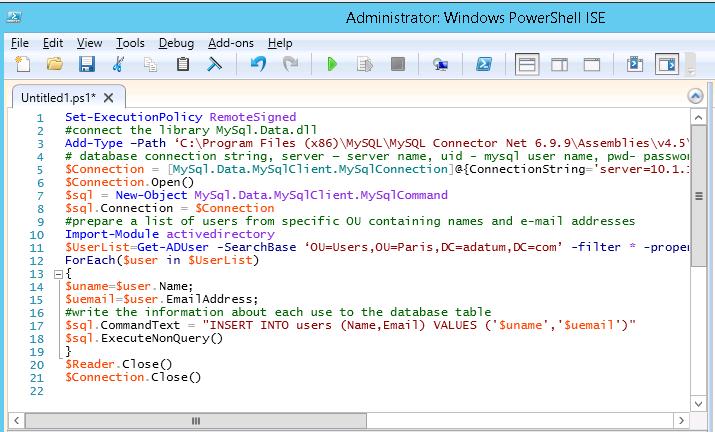
The following PowerShell script allows to connect to the database and write the list of users and their e-mails obtained from AD.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
#connect the library MySql.Data.dll
Add-Type –Path ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Connector Net 6.9.9\Assemblies\v4.5\MySql.Data.dll'
# database connection string, server — server name, uid - mysql user name, pwd- password, database — name of the database on the server
$Connection = [MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection]@{ConnectionString='server=10.1.1.13;uid=posh;pwd=P@ssw0rd;database=aduser'}
$Connection.Open()
$sql = New-Object MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand
$sql.Connection = $Connection
#prepare a list of users from specific OU containing names and e-mail addresses
Import-Module activedirectory
$UserList=Get-ADUser -SearchBase ‘OU=Users,OU=Paris,DC=adatum,DC=com’ -filter * -properties name, EmailAddress
ForEach($user in $UserList)
{
$uname=$user.Name;
$uemail=$user.EmailAddress;
#write the information about each use to the database table
$sql.CommandText = "INSERT INTO users (Name,Email) VALUES ('$uname','$uemail')"
$sql.ExecuteNonQuery()
}
$Reader.Close()
$Connection.Close()
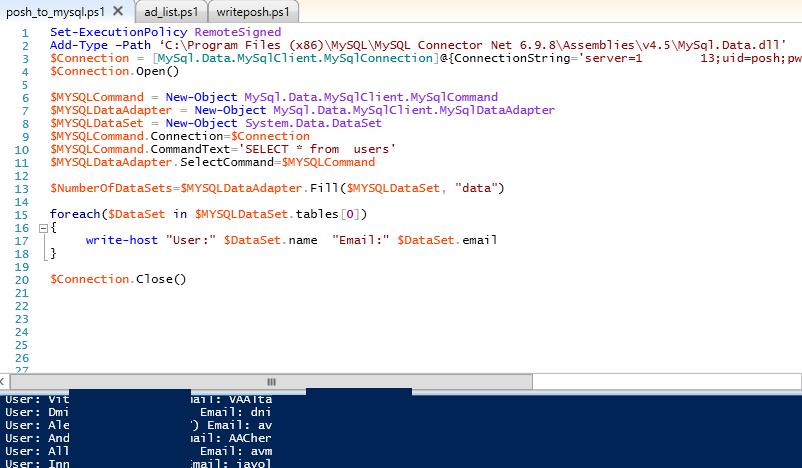
The following script is used to read the data previously entered to the database and to display them in PowerShell console. We have displayed the fields containing the names and e-mail addresses of the users:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Add-Type –Path ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Connector Net 6.9.9\Assemblies\v4.5\MySql.Data.dll'
$Connection = [MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection]@{ConnectionString='server=10.1.1.13;uid=posh;pwd=P@ssw0rd;database=aduser'}
$Connection.Open()
$MYSQLCommand = New-Object MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand
$MYSQLDataAdapter = New-Object MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlDataAdapter
$MYSQLDataSet = New-Object System.Data.DataSet
$MYSQLCommand.Connection=$Connection
$MYSQLCommand.CommandText='SELECT * from users'
$MYSQLDataAdapter.SelectCommand=$MYSQLCommand
$NumberOfDataSets=$MYSQLDataAdapter.Fill($MYSQLDataSet, "data")
foreach($DataSet in $MYSQLDataSet.tables[0])
{
write-host "User:" $DataSet.name "Email:" $DataSet.email
}
$Connection.Close()
In the next articles, we’ll consider the case of using MySQL database to collect and store information from Windows event logs ( Tracking Files Deletion using Audit Policy and MSSQL Database).
1 comment
Hi, I am learning my way around powershell and kind of new to trying to create my own script. I was kind of working my way around with your script and attempted write my own but I can’t seem to figure it out. I am basically trying to use powershell to query MySQL and check if Last_IO_Error, is Slave_IO_Running, Slave_SQL_Running and Seconds_Behind_Master=0 Would you happen to have any suggestions? Thanks Paul