If you are going to configure synchronization of your local (on-premises) Active Directory with Microsoft 365/Azure AD using Azure AD Connector (AADConnect), you must first check the object attributes in your on-premises ADDS for compatibility with Azure AD.
Microsoft has released a special Microsoft Office 365 IdFix tool (Directory Synchronization Error Remediation) for checking on-premises Active Directory instance. The IdFix tool allows you to scan your ADDS and find users, contacts, or groups that cannot be synced with Azure AD for some reason.
IdFix detects the most common errors in Active Directory object attributes:
- Invalid symbols in AD object names (including leading and trailing spaces);
- Duplicates;
- Invalid SMTP addresses, MailNickNames;
- Objects with attribute values that exceed acceptable limits;
- Correct routable UPN suffixes (userPrincipalName).
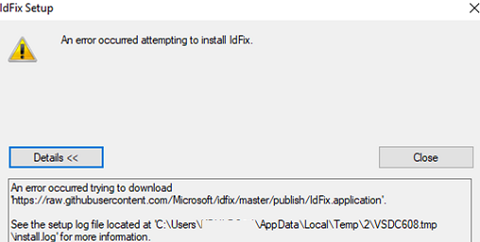
You can find IdFix on GitHub (https://github.com/microsoft/idfix) and download its setup.exe using the direct link. IdFix is a ClickOnce app, so internet access is required to install it. Otherwise, you will see this error:
An error occurred attempting to install IdFix Error: An error occurred trying to download 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Microsoft/idfix/master/publish/IdFix.application'
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings] "DisableCachingOfSSLPages"=dword:00000000
Use the command below:
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings" /v DisableCachingOfSSLPages /t reg_dword /d 00000000 /f
After that, the IDFix installation will start normally.
After you have finished working with IdFix, set the DisableCachingOfSSLPages value to 1.
You can install IdFix on any domain-joined computer. Run the tool and click Query.
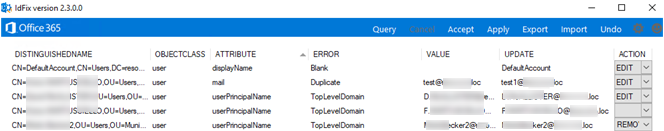
The IdFix will connect to your on-prem Active Directory domain and display a list of you need to fix before syncing with Azure.
In our example, IdFix found several objects AD objects with three types of errors:
- Empty displayName attribute of a user account (
displayName= Blank) - The same values of the mail attribute for several users (
mail=Duplicate) - Three users had non-routable userPrincipalName from .loc domain (
userPrincipalName=TopLevelDomain)
You may also see the following errors:
- Character – invalid symbols in an attribute
- Format – incorrect format of attribute values (for example, the invalid format of SMTP addresses)
- Length – the attribute length is exceeded
If you are going to sync discovered users with Azure AD, you need to fix these errors. Select the ACTION you want to apply to the AD object attributes you have found (Edit, Remove, Complete). If you selected Edit, you can specify a new attribute value in the Update box.
To apply the changes, click Accept -> Apply. The changes will be applied only to the entries that have values set in the Action field.
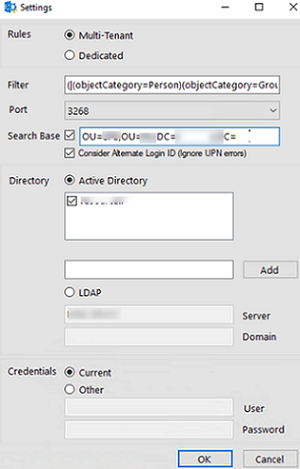
If you are going to sync only a part of your Active Directory with Azure, you can specify the criteria to select AD objects for analysis in the Settings (using an LDAP filter). Using Search Base, you can select the OU for analysis.
IdFix allows you to find and fix a lot of problems that may prevent user, contact, or group synchronization from on-premises Active Directory to Azure AD. Make sure you check your on-premises Active Directory when preparing for directory synchronization to Microsoft 365 via Azure AD Connect.