In some cases it is necessary to delete all entries from Windows event logs on a computer or a server. Of course, you can clear the system logs from the Event Viewer console GUI— Eventvwr.msc (right-click the log you would like to clear and select Clear Log). However, starting with Vista, Windows has been using several dozens of logs for different system components, and it is time-consuming to manually clear all of them in the Event Viewer. It is much easier to clear logs from the command prompt: using PowerShell or the built-in console tool wevtutil.
Clearing Event Logs With PowerShell
If you have PowerShell 3 installed (by default, it is installed in Windows 8 / Windows Server and higher), you can use Get-EventLog and Clear-EventLog cmdlets to get the list of event logs and clear them.
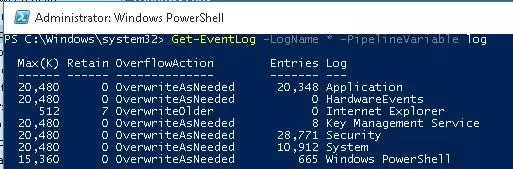
Start the PowerShell console with the administrator privileges and using the following command display the list of all standard event logs in the system with the maximum size and the number of events.
Get-EventLog –LogName *
To clear all entries from the specific event log (for example, System log), use this command:
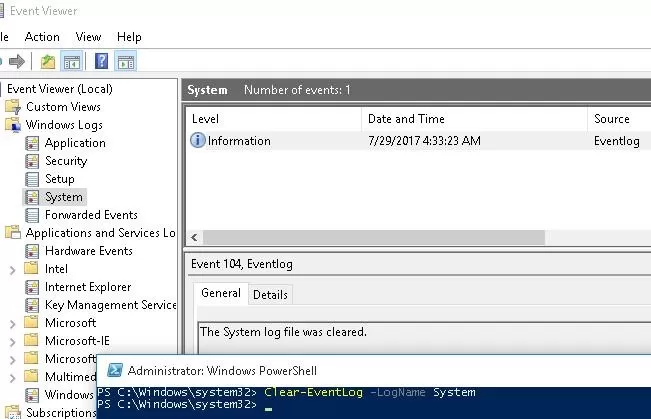
Clear-EventLog –LogName System
As a result, all events of this log will be deleted, and there will be only one event with the EventId 104 and the message “The System log file was cleared“.
To clear all event logs, you have to redirect the log names to the pipeline, but unfortunately, it is forbidden. So, we will have to use the ForEach cycle:
Get-EventLog -LogName * | ForEach { Clear-EventLog $_.Log }
Thus, all standard event logs will be cleared.
Clearing the Logs Using the console tool WevtUtil.exe
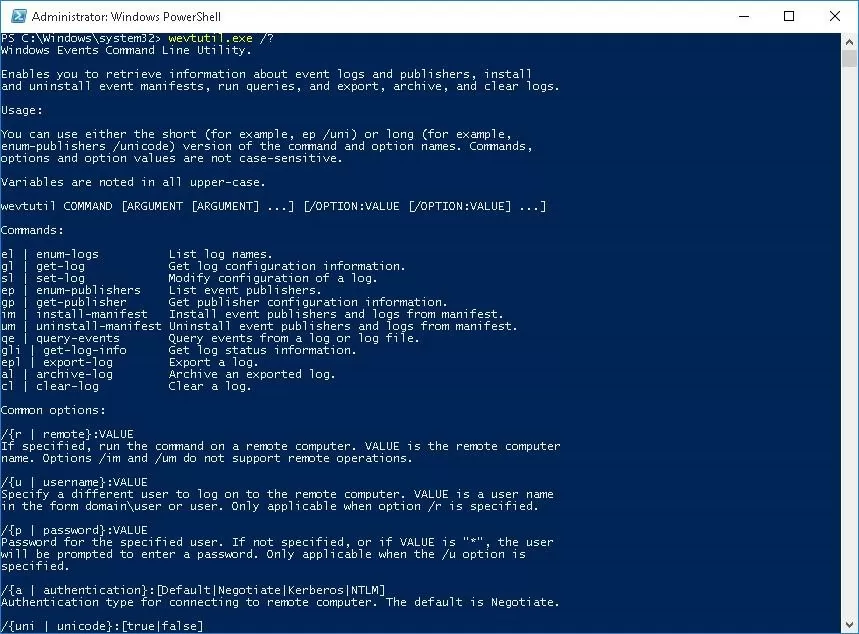
To work with the events, for a long time in Windows there have been a powerful command prompt utility WevtUtil.exe. Its syntax is a bit complicated for the first sight. Here, for example, that returns help of utilities:
To display the list of the logs registered in the system, run this command:
WevtUtil enum-logs
or its shorter version:
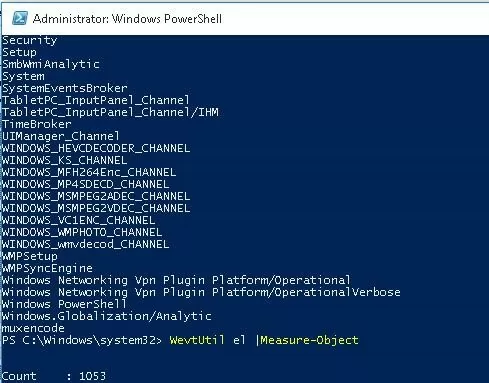
WevtUtil el
Quite an impressive list of logs will be displayed on the screen.
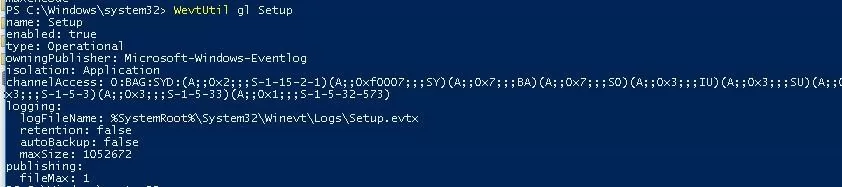
You can get a detailed information on the specific log:
WevtUtil gl Setup
Here is how you clear the events in the specific log:
WevtUtil cl Setup
Before you clear the events, you can backup them by save to a file:
WevtUtil cl Setup /bu:SetupLog_Bak.evtx
To clear all logs at once, you can use Get-WinEvent PowerShell cmdlet to get all log objects and Wevtutil.exe to clear them:
Get-WinEvent -ListLog * -Force | % { Wevtutil.exe cl $_.LogName }
or
Wevtutil el | ForEach { wevtutil cl “$_”}
You can clear the logs using the standard command prompt as well:
for /F "tokens=*" %1 in ('wevtutil.exe el') DO wevtutil.exe cl "%1"
1 comment
Very good guide for managing LOG files.