In this article, we will show how to track an event of launching a certain program (process) in Windows and perform an action (run a script, command, program, send an email, etc.). As an example, we will track the launch of the notepad.exe process. And when a user opens Notepad, Windows will automatically run a specific PowerShell script.
First of all, configure the process audit policy on Windows. You can configure audit policy on a stand-alone computer using the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc). If you want to configure a policy on computers and servers in your AD domain, use the Group Policy Management console (gpmc.msc).
- Go to Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Audit Policy;
- Open Audit process tracking properties and enable it for Success events;
- Apply Group Policy settings by running:
gpupdate /force
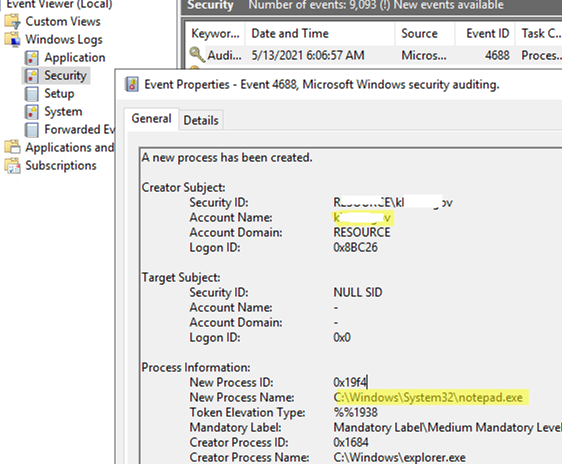
Now, when starting any process in Windows, an event with the EventID 4688 (A new process has been created) will appear in the Event Viewer -> Windows Logs -> Security. The event shows who has run the process (Account name), the name of the process (New Process Name), and the name of the parent process (Creator Process Name).
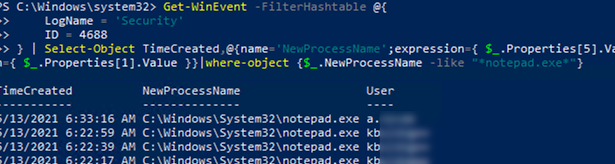
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{
LogName = 'Security'
ID = 4688
} | Select-Object TimeCreated,@{name='NewProcessName';expression={ $_.Properties[5].Value }}, @{name='User';expression={ $_.Properties[1].Value }}|where-object {$_.NewProcessName –like “*notepad.exe*”}
As a result, we got the history of launching the program by users on this computer.
Then create a new task in the Task Scheduler that will run if an event with the EventID 4688 appears.
- Open the Task Scheduler (
taskschd.msc) and create a new task -> Create Task; - Provide the task name and specify that it must be run for all users (When running the task, use the following user account -> BUILTIN\Users). If you create a task using GPO, use this format:
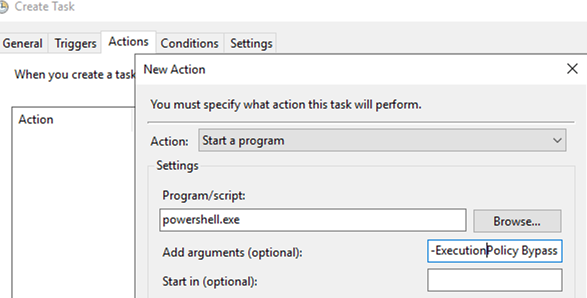
%LogonDomain%\%LogonUser%; - On the Actions tab, set the action you want to perform. In this example, I will run a PowerShell script (call
powershell.exewith attributes:-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -file "C:\PS\ProcessRunEvent.ps1); - Then bind the task to a Windows event. Go to Triggers tab, select New -> On an event -> Custom -> New Event Filter;
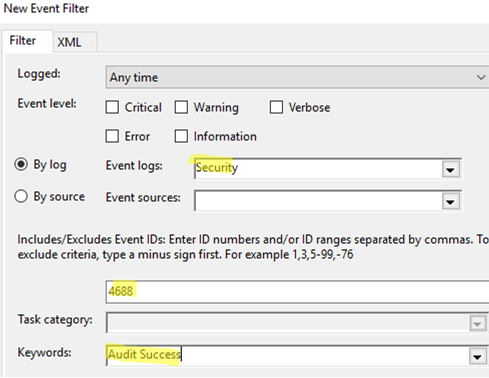
- In the next window, specify the following event filter options:
Event logs:Security
Event ID:4688
Keywords:Audit Success
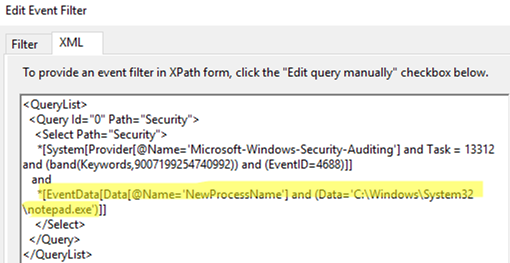
- Then go to the XML tab and enable the Edit query manually option. Edit the query by adding the following line to the filter:
and *[EventData[Data[@Name='NewProcessName'] and (Data='C:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe')]] - You will get the following XML query:
<QueryList> <Query Id="0" Path="Security"> <Select Path="Security"> *[System[Provider[@Name='Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing'] and Task = 13312 and (band(Keywords,9007199254740992)) and (EventID=4688)]] and *[EventData[Data[@Name='NewProcessName'] and (Data='C:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe')]] </Select> </Query> </QueryList>
- Save the task.
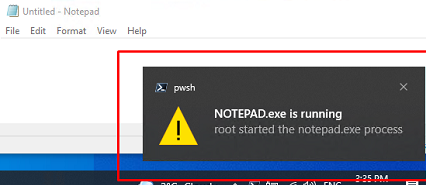
Try to run the notepad.exe. Each time a user opens the Notepad, your PowerShell script will automatically run.
A process has exited.Earlier we showed a PowerShell script to automatically restart a process if it stops. The solution tracking a run/stop event of a process is more elegant and doesn’t require a PowerShell script to monitor running Windows processes.
1 comment
The program I’m trying to audit has spaces and a “&” in the path wich seems to lead to an error when setting up the trigger. is there a solution for this?