You can use the open-source usbipd-win project to access a computer’s physical USB devices from the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2) or Hyper-V virtual machine. This tool allows you to pass-through an external USB device connected to the Windows host to any Linux distribution (running as WSL) or to a virtual machine. This allows performing any actions with USB devices from virtual machines or Linux environment (flashing Android devices, using ADB and Fastboot, accessing smart cards, working with Arduino hardware, etc.).
Usbipd-win uses the TCP/IP protocol to forward the USB device traffic over a virtual network interface between the VM/WSL and the host Windows operating system. First, we’ll show how to install the usbipd-win server on a Windows host, then we’ll install a USB/IP client on Linux (WSL) and attach a shared USB device to the Linux VM (WSL).
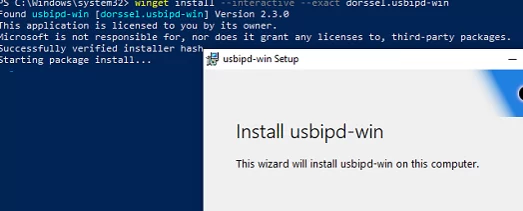
Usbipd-win project is available on GitHub (https://github.com/dorssel/usbipd-win). You can download and install it manually (an MSI installation file is available), but it’s much quicker to install it using the built-in Winget package manager.
winget install --interactive --exact dorssel.usbipd-win
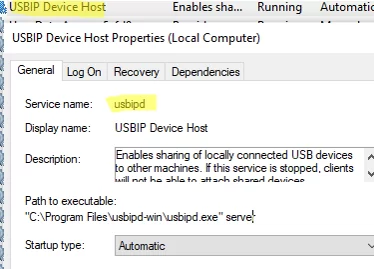
The program will create a separate usbipd (USBIP Device Host) service on Windows: "C:\Program Files\usbipd-win\usbipd.exe" which listens on TCP port 3240
An additional rule has been created in Windows Defender Firewall for the usbipd.exe to allow access to TCP port 3240 from computers on the local network.
Now let’s configure USBIP support in Windows Subsystem for the Linux environment. Make sure that the kernel version in your image is at least 5.10.60.1 (our demo example uses WSL 2 with an Ubuntu 22.04 LTS image):
$ uname -a
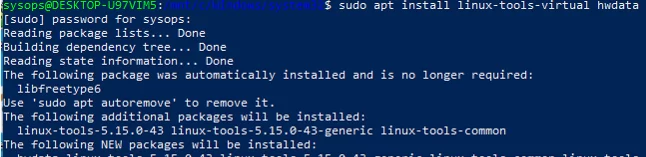
Now you need to install USB/IP tools and USB hardware ID base.
$ sudo apt install linux-tools-virtual hwdata
$ sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/local/bin/usbip usbip `ls /usr/lib/linux-tools/*/usbip | tail -n1` 20
$ sudo apt-get install usbip hwdata usbutils
Install USB/IP tools in an rpm-based WSL image (CentOS/Oracle Linux):
$ sudo rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org
$ sudo rpm -ivh http://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-3.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm
$ sudo yum install kmod-usbip
$ sudo yum install usbip-utils
$ sudo yum install hwdata
Now open an elevated command prompt on the host Windows computer and list the USB devices:
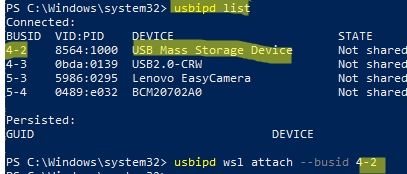
usbipd wsl list
As you can see, none of the USB devices are shared (Not shared). You may share the USB device by its BUSID. In my example, I’d like to passthrough the USB Mass Storage Device with BUISID 4-2 into WSL.
usbipd wsl attach --busid 4-2
- If you are using WSL 1 (not supported by usbip) you will get an error.
sbipd: error: The specified WSL distribution is using WSL 1, but WSL 2 is required. Learn how to upgrade at https://docs.microsoft.com/windows/wsl/basic-commands#set-wsl-version-to-1-or-2.
- If an error appears:
usbipd: error: WSL kernel is not USBIP capable, update WSL system with the following command:
wsl --update
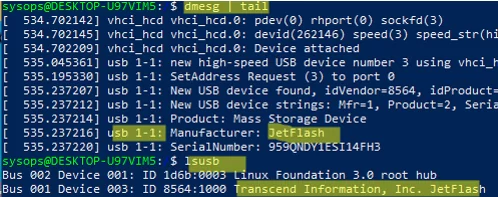
Check that your USB flash drive is connected to WSL:
$ dmesg | tail
$ lsusb
If you would like to share your USB device with another computer running Linux over the network (it can be a virtual machine with a Linux guest on Hyper-V or any other hypervisor), first list the available USB devices on a remote Windows host:
$ usbip list --remote=192.168.13.21
You can now mount the required USB device by its ID:
$ sudo usbip attach -remote=192.168.13.21 --busid=4-2
In this example, the IP address of the Windows host on which the usbipd-win server is running is specified.
The shared USB device should now be visible to your Linux tools.
To disable USB device sharing in Windows:
usbipd wsl detach --busid 4-2
Please note that USB drives connected in this way are not recognized as block devices in WSL. Check this using the lsblk command. The fact is that the WSL kernel does not have a driver for USB drives (to add them, you will have to rebuild the kernel).
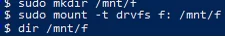
Therefore, you must use the following commands to mount an external USB flash drive, floppy disc, or SD card in WSL:
$ sudo mkdir /mnt/f
$ sudo mount -t drvfs f: /mnt/f
Thus, usbipd-win can be used to pass-through physical USB devices from a physical Windows host to WSL, virtual machine, or Linux computers over a network using the USBOverIP protocol.