In this article we’ll look on the disk, partition and volume management from PowerShell console. You can perform from PowerShell all the operations of managing local disks and partitions, that you are used to performing from the “Disk Management” GUI (diskmgmt.msc) or from the diskpart.exe command line tool. Disk management cmdlets are included in the Storage module available in PowerShell 3.0. We’ll consider how to initialize a disk, create a partition table on it, create a volume and format it. The commands given below will work in Windows 10 / Server 2016 and Windows 8.1 / Server 2012 R2 (for previous Windows versions you will have to update PowerShell first).
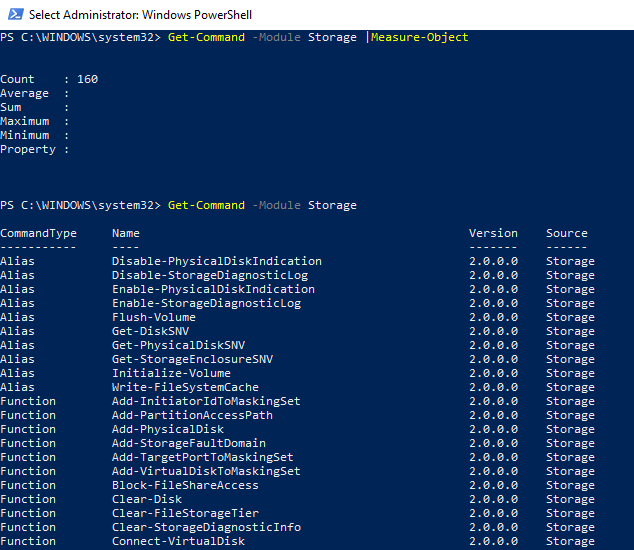
There are 160 PowerShell cmdlets in the Storage module in Windows 10. To display all available commands related to disk management, run the following command:
Get-Command -Module Storage
PowerShell: List Local Disks and Partitions
First of all, try to display the list of local disks available in your system at the logical level. To do it, run this command:
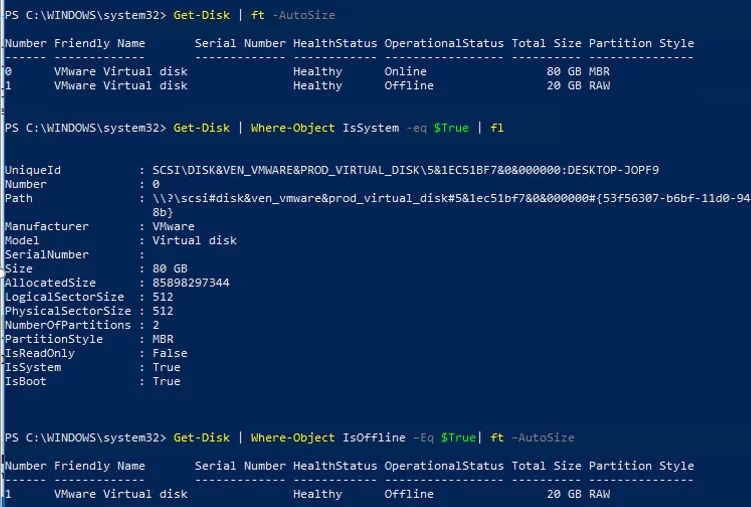
Get-Disk | ft -AutoSize
To select only the system disk on which Windows is installed, enter the following command:
Get-Disk | Where-Object IsSystem -eq $True | fl
As you can see, the command has returned the following attributes of the system disk (you can use them in the selection as well):
UniqueId : SCSI\DISK&VEN_VMWARE&PROD_VIRTUAL_DISK\5&1EC51BF7&0&000000:DESKTOP-JOPF9
Number : 0
Path : \\?\scsi#disk&ven_vmware&prod_virtual_disk#5&1ec42ba7&0&000000#{21f23456-a6bf-12d0-94f2-001efb8b}
Manufacturer : VMware
Model : Virtual disk
SerialNumber :
Size : 98 GB
AllocatedSize : 98432321434
LogicalSectorSize : 512
PhysicalSectorSize : 512
NumberOfPartitions : 2
PartitionStyle : MBR
IsReadOnly : False
IsSystem : True
IsBoot : True
You can display Offline disks only:
Get-Disk | Where-Object IsOffline –Eq $True| ft –AutoSize
If you need the information about physical disks (the characteristics and status of physical disks on a computer), use Get-PhysicalDisk cmdlet (previously we showed how to detect a failed physical disk in Storage Spaces Direct using Get-PhysicalDisk cmdlet and how to use it then configure a fault tolerant S2D storage).
You can detect the type of connected disk: SSD, HDD (usually connected over SATA bus) or a USB flash drive (UnSpecified media type).
DeviceId Model MediaType BusType Size ——— —— ——— ——- —- 0 TOSHIBA MK3775VSXP HDD SATA 500156374016 1 Samsung SSD 840 PRO Series SSD SATA 128060514304 2 Transcend UnSpecified USB 128169757184
You can display the list of partitions on all disks:
Get-Partition
Or partitions on the specified disks only:
Get-Partition –DiskNumber 1,2
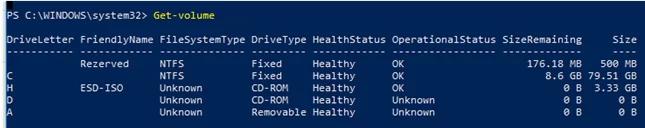
To display the list of all volumes in Windows, run this command:
Get-Volume
Disk Initialization in PowerShell
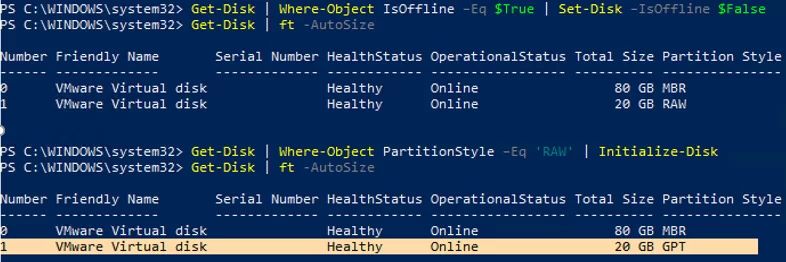
In the previous example you have seen that one of the disks is Offline and has a RAW label in the Partition Style column. Let’s try to initialize it, create a GPT or MBR partition table and create a new partition on it.
First of all, you must get the disk Online:
Get-Disk | Where-Object IsOffline –Eq $True | Set-Disk –IsOffline $False
Now you can initialize it (its index is 1):
Initialize-Disk -Number 1
By default, a GPT (GUID) partition table is created on a disk, but if you need an MBR one, run this command:
Initialize-Disk 1 –PartitionStyle MBR
In order not to specify the disk number, you can initialize all disks with the RAW partition table:
Get-Disk | Where-Object PartitionStyle –Eq 'RAW' | Initialize-Disk
How to Create Partitions on a Disk?
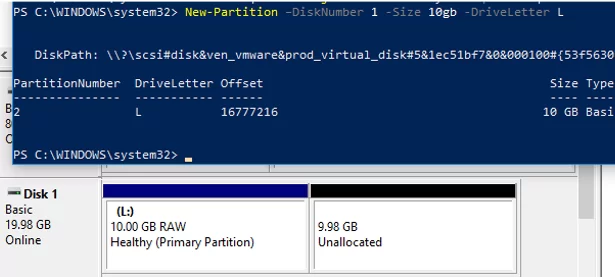
To create a new partition on a disk, the New-Partition cmdlet is used. Let’s create a 10 GB partition and assign the letter L: to it:
New-Partition –DiskNumber 1 -Size 10gb -DriveLetter L
If you want the partition to occupy all available disk space, use the UseMaximumSize attribute. To assign a letter automatically, the AssignDriveLetter parameter is used (sometimes Windows doesn’t assign a drive letter automatically).
New-Partition –DiskNumber 1 -AssignDriveLetter –UseMaximumSize
You can change the assigned letter using this command:
Set-Partition –DriveLetter L -NewDriveLetter U
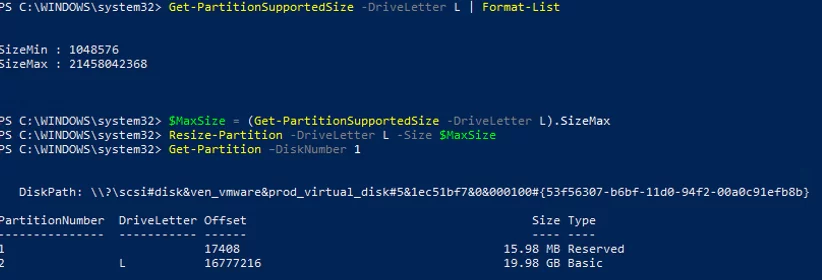
If you want to expand the existing partition, first of all display the available unallocated space to extend this partition:
Get-PartitionSupportedSize -DriveLetter L | Format-List
Then you can extend the size of the partition to the maximum:
$MaxSize = (Get-PartitionSupportedSize -DriveLetter L).SizeMax
Resize-Partition -DriveLetter L -Size $MaxSize
If you want to make a partition active, this command is used:
Set-Partition -DriveLetter U -IsActive $true
Formatting a partition with PowerShell
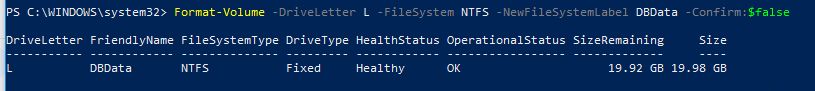
Let’s format new partition in the NTFS and set the DBData volume label:
Format-Volume -DriveLetter L -FileSystem NTFS -NewFileSystemLabel DBData -Confirm:$false
How to Remove Partitions from a Disk?
To remove all partitions on disks 1 and 2 without confirmation, run this command:
Get-Partition –DiskNumber 1,2 | Remove-Partition -Confirm:$false
To delete all partitions from disks and completely clear data, run the command
Clear-Disk -Number 1 -RemoveData -Confirm:$false
If there are OEM partitions on a disk (OEM recovery partition, EFI partition, System Reserved), use the RemoveOEM parameter to remove them:
Clear-Disk -Number 1 -RemoveData –RemoveOEM
The next PowerShell one-liner will initialize all new connected RAW-type disks, create the partition table on them and create an NTFS partitions with the maximum available size. It is convenient to use it when connecting a new disk:
Get-Disk |Where-Object PartitionStyle -eq 'RAW' |Initialize-Disk -PartitionStyle MBR -PassThru |New-Partition -AssignDriveLetter -UseMaximumSize |Format-Volume -FileSystem NTFS -Confirm:$false


5 comments
thank you, this was very helpful
Thanks so much, your post help me so much,
i did the follow script for shrink and create a new partition with free space:
Exmaples: Disk = 0, Driveletter=K
New-Partition -DiskNumber 0 -UseMaximumSize -DriveLetter k
maybe this can help other people. 🙂
It would’ve been more helpful to include commands that show how to automatically select the correct eg unformatted disk. Instead, the article shows that we have to figure out which disk which defeats the purpose of automating the tasks.
I have a script I use to backup data using robocopy. Because it stores critical/sensitive data, I prefer to hide the partition rather than allowing Windows to mount it automatically, and only use the script to unhide the partition, backup the date with robocopy, and hide the partition again. I use the HDD/SSD serial number in order to mount the drive and run the script.
You can get the serial number with:
Get-Disk | Select-Object Number,SerialNumber
Here’s part of the code I use that work both old and recent Powershell versions. The storage device serial number is represented as ’53R1ALNUMB3R’. The drive has two partitions, one small FAT16 and the “hidden” NTFS (partition 3). I run this with elevated privileges:
# To maintain compatibility with old Powershell versions
if ( $PSVersionTable.PSVersion.Major -le 4 )
{ Get-Disk | Where-Object SerialNumber -EQ 53R1ALNUMB3R | Get-Partition | Where-Object PartitionNumber -EQ 3 | Set-Partition -IsHidden $false }
else
# For Powershell v5 or later
{ Get-Disk -SerialNumber 53R1ALNUMB3R | Set-Partition -PartitionNumber 3 -IsHidden $false }
I recall there being some commands that can allow one to reset and recreate some sort of system log in the SRP that can grow to fill up the entire SRP free space and then interfere with system operations such as Windows Backup and Update. I used them a couple years ago when Backup broke as a result. I remember you go into disk management, add a drive letter to the SRP, and then do these commands. One of the commands let you see the existence and size of this mystery log. Once done, remove the drive letter, things work again. Anyone recall what the commands are?