PHP-FPM (Fast Process Manager) is a separate implementation of FastCGI to run PHP scripts. You can use a combination of NGINX web server (processing static) and PHP-FPM to build a faster and high performance web server for your websites than on the LAMP stack (NGINX, Apache and mod_php module).
In this article we will look at how to install and optimize the LEMP stack (NGINX + PHP-FPM + MariaDB/MySQL) for hosting a high-load web project on a server running Linux CentOS 7.
Install and Configure Nginx as a Web Server
Since a newly installed CentOS server is used for installation, connect the popular EPEL repository and update all packages on the server.
# yum install epel-release -y
# yum update -y
To install the latest Nginx version, connect the developer repository by running this command:
# rpm -Uvh http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-7-0.el7.ngx.noarch.rpm
Or create the repository configuration file manually (/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo). Add the following lines to the file:
[nginx] name=nginx repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
If you are using CentOS 8, change the version in the URL.
Install Nginx web server package using yum (or dnf) package manager:
# yum install nginx -y
Then run nginx and add it to startup using systemctl:
# systemctl start nginx
# systemctl enable nginx
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
To check that the web server is running, open the server IP address in your browser.
If you don’t see this test page, check the settings of allowed services, ports and zones in firewalld on your server.
Make a configuration file for a separate domain woshub-linux.com. Create a separate directory for the site and the config file:
# mkdir -p /var/www/woshub-linux.com && mkdir -p /var/www/woshub-linux.com/log
Open the configuration file:
# nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/woshub-linux.com.conf
And add the following contents to it:
server {
listen 80;
server_name woshub-linux.com;
root /var/www/woshub-linux.com;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
access_log /var/www/woshub-linux.com/log/access.log main;
error_log /var/www/woshub-linux.com/log/error.log;
location / {
return 301 https://woshub-linux.com$request_uri;
}
location ~* ^.+.(js|css|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico|woff)$ {
return 301 https://woshub-linux.com$request_uri;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
return 301 https://woshub-linux.com$request_uri;
}
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
rewrite ^ /robots.txt break;
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.woshub-linux.com;
rewrite ^ https://woshub-linux.com$request_uri? permanent;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name woshub-linux.com;
root /var/www/woshub-linux.com;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
access_log /var/www/woshub-linux.com/log/ssl-access.log main;
error_log /var/www/woshub-linux.com/log/ssl-error.log;
keepalive_timeout 60;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/woshub-linux.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/woshub-linux.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:AES128-GCM-SHA256:AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES128-SHA256:AES256-SHA256:AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA:AES:CAMELLIA:DES-CBC3-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!MD5:!PSK:!aECDH:!EDH-DSS-DES-CBC3-SHA:!EDH-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:!KRB5-DES-CBC3-SHA';
add_header Strict-Transport-Security 'max-age=604800';
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
location ~* ^.+.(js|css|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico|woff)$ {
access_log off;
expires max;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php-fpm/php-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT /var/www/woshub-linux.com;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /var/www/woshub-linux.com/$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_TRANSLATED /var/www/woshub-linux.com/$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length;
fastcgi_param HTTPS on;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_ignore_client_abort off;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 60;
fastcgi_send_timeout 180;
fastcgi_read_timeout 180;
fastcgi_buffer_size 128k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 256k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 256k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
}
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name www.woshub-linux.com;
rewrite ^ https://woshub-linux.com$request_uri? permanent;
}The configuration file contains settings to access site using the secure HTTP protocol access since many popular CMS use it by default. Later you can install and configure a free Let’s Encrypt certificate (just like we installed a Let’s Encrypt certificate for a website in IIS in Windows Server).
Install PHP-FPM
Nginx has no built-in PHP handler, so we must install php-fpm and some PHP modules to process PHP scripts.
In its turn, Nginx is returns static more efficiently. In our configuration nginx will be a proxy server (a caching and front-end server) and php-fpm will serve as a back-end.
Use the REMI repository to install newer php versions:
# rpm -ivh http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm
After the installation, edit the /etc/yum.repos.d/remi-php74.repo file:
Run php-fpm and popular php module installation:
# yum install php-fpm php-cli php-mysql php-gd php-ldap php-odbc php-pdo php-opcache php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-mbstring php-snmp php-soap php-zip
Start php-fpm daemon and add it to startup:
# systemctl start php-fpm
# systemctl enable php-fpm
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/php-fpm.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service.
To make sure if the service has been started, run this command:
# lsof -i:9000
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME php-fpm 1551 root 7u IPv4 2078435 0t0 TCP localhost:cslistener (LISTEN) php-fpm 1552 apache 9u IPv4 2078435 0t0 TCP localhost:cslistener (LISTEN) php-fpm 1553 apache 9u IPv4 2078435 0t0 TCP localhost:cslistener (LISTEN) php-fpm 1554 apache 9u IPv4 2078435 0t0 TCP localhost:cslistener (LISTEN) php-fpm 1555 apache 9u IPv4 2078435 0t0 TCP localhost:cslistener (LISTEN) php-fpm 1556 apache 9u IPv4 2078435 0t0 TCP localhost:cslistener (LISTEN)
Run php-fpm using a unix socket. Delete the line “listen = 127.0.0.1:9000” from /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf and add the following:
listen = /var/run/php-fpm/php-fpm.sock listen.mode = 0660 listen.owner = nginx listen.group = nginx
To start php-fpm as a non-apache user (by default), specify these parameters in the configuration file:
user = nginx group = nginx
After changing the php-fpm config file, restart the service:
# systemctl restart php-fpm
Install MySQL/MariaDB on a Web Server
We’ll skip this step.
Configuring Nginx + PHP-FPM for High Load
In order for your web server can process a large number of client requests (high traffic website), it is important to properly configure nginx and php-fpm.
Nginx Configuration
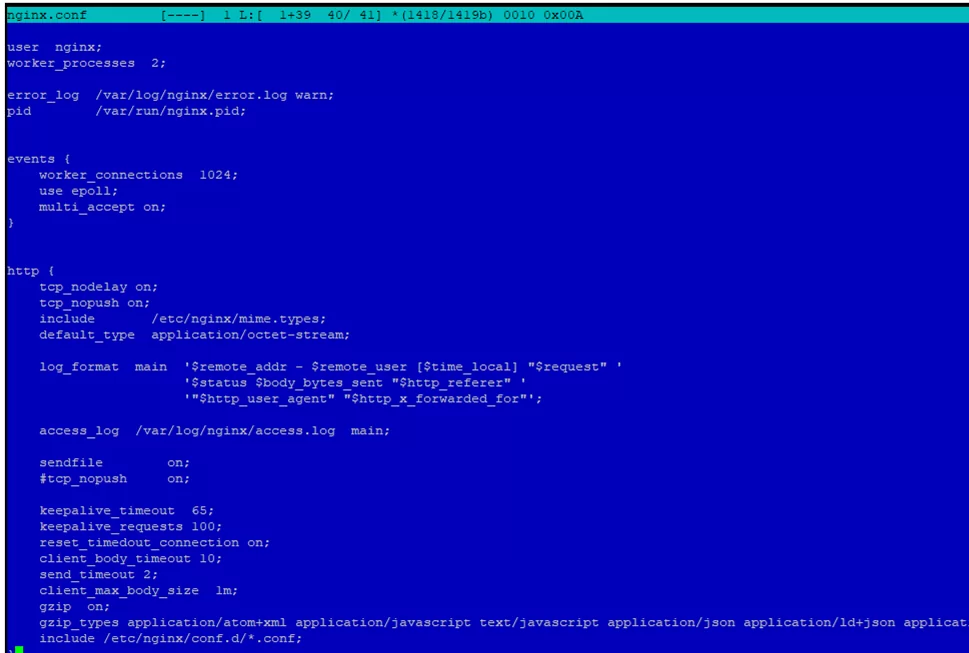
Open /etc/nginx/nginx.conf file and change Nginx configuration as follows:
worker_processes 2;— set the number of worker processes equal to the number of cores on your server;worker_connections 1024;— set the number of connections for one working process (set the value from 1024 to 4096);use epoll;— is an optimal connection method in Linuxmulti_accept on;— nginx will accept the maximum number of connections.
The http block:
tcp_nodelay on;— sends headers and the beginning of the file in one package;tcp_nopush on;
Enable gzip compression for web-projects containing a lot of static files:
gzip on;
Add different file types to pass all googlespeed checks:
gzip_types application/atom+xml application/javascript text/javascript application/json application/ld+json application/manifest+json application/rss+xml application/vnd.geo+json font/ttf application/x-font-ttf application/vnd.ms-fontobject application/font-woff application/font-woff2 application/x-web-app-manifest+json application/xhtml+xml application/xml font/opentype image/bmp image/svg+xml image/x-icon text/cache-manifest text/css text/plain text/vcard text/vnd.rim.location.xloc text/vnd.wap.wml text/vtt text/x-component text/x-cross-domain-policy;
Change timeout settings:
keepalive_timeout 30;— a web server will wait for 30 seconds before closing a keepalive connection;keepalive_requests 100;is the maximum number of keepalive requests from one client;reset_timedout_connection on;— enable this parameter if you don’t want the connections from a client that stopped responding to be reset;client_body_timeout 10;— a web server will wait for a client to confirm the request for 10 seconds until the connection is reset;send_timeout 2;— if a client stops reading web server response, nginx will reset the connection.
If your website is not designed for uploading large files, set the limit using nginx:
client_max_body_size 2m;— a server will not accept requests over 2 MB
If the content of your project doesn’t change often, you can use the ‘expires max;’ caching or add the corresponding option to the configuration file of your host for the file types you need, for example:
location ~* ^.+.(js|css|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico|woff)$ {
expires 7d;
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~Cache for the specified file types will be stored for 7 days.
Don’t forget to restart nginx after making any changes.
# systemctl restart nginx
Php-fpm Configuration
When installing php-fpm, you switched it to unix socket right away. It significantly boosts the performance. According to the estimates, the productivity grows 2 or 3 times. Other php-fpm parameters must be set for each project individually. Let’s consider a configuration example for a single-core (vCPU) server with 1,024 MB RAM.
You can allocate about 512 MB for php-fpm, leaving the rest for your database and nginx.
Add the following to the configuration file /etc/php-fpm/www.conf:
pm.max_children = 18is the maximum number of child processespm.start_servers = 6is the number of child processes created at the startuppm.min_spare_servers = 4is the minimum number of inactive server processespm.max_spare_servers = 16is the maximum number of inactive server processespm.max_requests = 400is the number of child process requests, after which the process will be restarted
I haven’t described how to optimize MariaDB settings, as there is the corresponding article on this website. I have set my.cnf parameters for my project based on the article, and the database has shown excellent performance results.
After running your website, you will see by the naked eye that nginx + php-fpm will process your requests and return webpages much faster than apache2 + mod_php.
2 comments
After trying to restart nginx I get: Job for nginx.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See “systemctl status nginx.service” and “journalctl -xe” for details.
Help please…
Can you show us what error you have by typing “journalctl -xe ” or “systemctl status nginx.service” on your terminal?