In this article we will show how to configure routing and manage network routes on Linux using the ip command on Linux CentOS (how to view the routing table, add/remove static routes, etc.). The article is applicable to any other Linux distro with ip tool (Red Hat, Fedora, etc.)
ip command instead of route. The route command doesn’t allow to configure advanced routing features (like routing policies) and cannot show special routing settings if they were set using the ip tool.How to View the Network Routing Table in Linux?
To display the current routing table in Linux, run this command:
# ip route
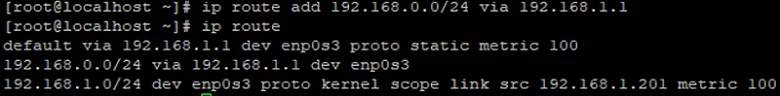
default via 192.168.1.1 dev enp0s3is the default gateway using the enp0s3 interface in this example. If the target IP address does not have a static route in the routing table, the packet is sent through that gateway (the default route);192.168.1.0/24 dev enp0s3 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.201is a static route for the 192.168.1.0/24 network through the interface 192.168.1.201;proto kernelis a route created by the kernel (proto static– the route added by an administrator);metricis the route priority (the less is the metric value, the higher the priority is). If there are two routes with the same metric (never do it!), the kernel will select routes randomly.
To find out which interface (gateway) is used to routing traffic to the specific IP address, the following command is used:
# ip route get 192.168.2.45
192.168.2.45 via 192.168.1.1 dev enp0s3 src 192.168.1.201
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 kernel parameter.Adding and Removing Static Routes in Linux
To add a new route to a specific IP network in the Linux routing table, run this command:
# ip route add 192.168.0.0/24 via 192.168.1.1
Thus, we will add the route for the 192.168.0.0/24 IP network through the gateway 192.168.1.1.
ip pro ad instead of ip route add.You can also add a separate static route for a single IP address (host):
# ip route add 192.168.1.0 via 192.168.1.1
You can create a null route similar to Cisco (ip route null0). The packets sent to this network are dropped due to No route to host:
# ip route add blackhole 10.1.20.0/24
The routes added using this method are temporary and will work until you restart the network service or the server.
To remove a static route created manually, run the following command:
# ip route del 192.168.0.0/24
As you can see, the route has been removed from the Linux routing table.
To add a persistent route, you must create a file for the route, or add a rule to the rc.local file (run on host startup).
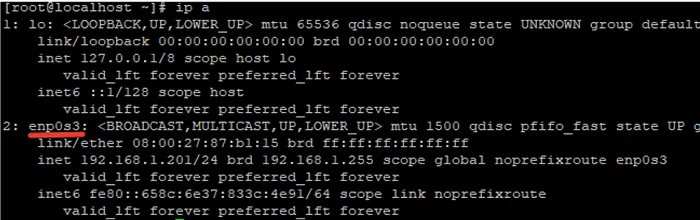
To add a permanent static route, you need a name of the network interface to be used for the routing. You can get the network interface name using this command:
# ip a
In my case, it is enp0s3.
Then open the following file:
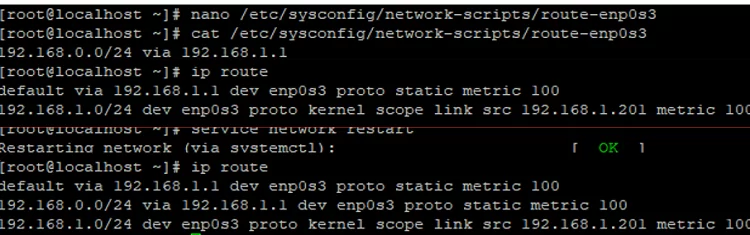
# nano /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-enp0s3
And add the line containing the route here:
192.168.0.0/24 via 192.168.1.1
After you have added the route to the file, restart the network service:
# service network restart
After restarting the network, a static route appeared in the routing table.
You can also use a command to add a new route to the rc.local file in order to automatically add static route when the server boot. Open the file:
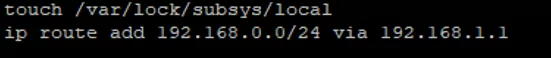
# nano /etc/rc.local
And enter the command that adds the static route:
# ip route add 192.168.0.0/24 via 192.168.1.1
Then if your server is restarted, the route will be automatically added during the system boot.
Modifying an Existing Route Entry in Linux
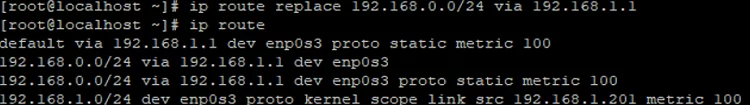
To change an existing route, you can use the ip route replace command:
# ip route replace 192.168.0.0/24 via 192.168.1.1
To reset all temporary routes in the routing table, just restart the network service:
# service network restart
Restarting network (via systemctl): [ OK ]
# ip route
default via 192.168.1.1 dev enp0s3 proto static metric 100 192.168.0.0/24 via 192.168.1.1 dev enp0s3 proto static metric 100 192.168.1.0/24 dev enp0s3 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.201 metric 100
How to Change the Default Route or Default Gateway on Linux?
You can remove a default route using the ip route del command:
# ip route del default via 192.168.1.1 dev enp0s3
To set a new default route, the following command is used in CentOS/RHEL Linux:
# ip route add default via 192.168.1.2 (a route via gateway IP address)
# ip route add default via enp0s3 (a route using a device name)
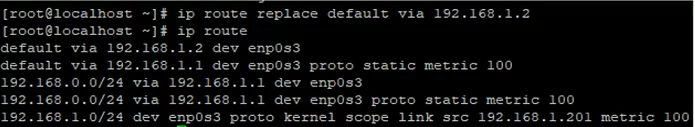
To change the default route settings, this command is used:
# ip route replace default via 192.168.1.2


1 comment
hi dear can i use my server to route packt and serv auter services in the samme timme if somme on can help 🙂