You can use the SFC (System File Checker) and DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) commands to check and repair the integrity of system files and Component Store of your Windows (Windows Server) image. These tools can be extremely useful if your Windows is unstable, won’t boot, errors appear when you try to run built-in apps or services, after a virus infection, etc.
In this article, we’ll take a look at how to use the SFC /ScanNow, DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth, or Repair-WindowsImage -Online -RestoreHealth commands to repair image and system files on Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2022/2019/2016.
- SFC /ScanNow: Using System File Checker to Repair Windows System Files
- Check Windows Component Store Health Using DISM
- Repair Windows Image Using DISM /RestoreHealth
- DISM /RestoreHealth: The Source Files Could Not Be Found
- Repair-WindowsImage: Repairing Windows Image Component Store with PowerShell
- Use DISM Offline to Repair Windows Image
SFC /ScanNow: Using System File Checker to Repair Windows System Files
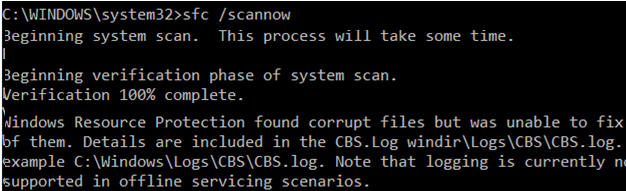
It is recommended to use the DISM command to restore Windows after you have checked the integrity of your system files using the SFC tool. The sfc /scannow command scans protected system files and if they are missing or corrupted it tries to restore their original copies versions the Windows Component Store (C:\Windows\WinSxS folder).
%windir%\logs\cbs\cbs.log . All SFC entries in the CBS.log file are tagged with [SR]. To select only SFC-related entries from the log, run the command:findstr /c:"[SR]" %windir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log >"%userprofile%\Desktop\sfc.txt"
If sfc /scannow command returns the error “Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files but was unable to fix some of them“, it is likely that the tool could not get the necessary files from the Windows Component Store (see the image below).
In this case, you can try to repair the Component Store of your Windows image using the DISM.exe command.
After repairing the Windows image, you can try using SFC to restore your system files.
Check Windows Component Store Health Using DISM
The DISM /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth switch is used to scan the Windows image for errors and fix them. DISM commands must be run from the elevated command prompt.
Run the following command to check if there are any flags of corruption of the Windows image Component Store (not applicable for Windows 7/Server 2008R2). This command checks the CBS flag set by one of the system maintenance processes.
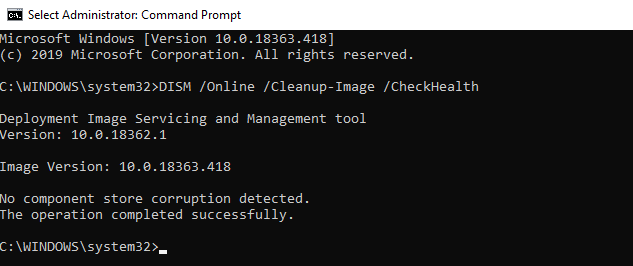
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth
This command doesn’t perform a full scan of the Component Store. The command only checks if your Windows image is flagged as corrupted and if it is possible to fix it. No changes are made to the image.
In this example, the command has returned that the Windows 10 image has no corruptions:
No component store corruption detected. The operation completed successfully.
To run a full scan of the Windows Component Store health, run the command:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth
The command to check the Windows image can take quite a long time (10-30 minutes). And will return one of three results:
- No component store corruption detected – DISM found no errors in the component store;
- The component store is repairable – DISM has encountered errors in the Component Store and can fix them;
- The component store is not repairable – DISM cannot fix the Windows Component Store (try using a newer version of DISM or you will have to restore a Windows image from a backup, reset or completely reinstall your Windows instance).
In some cases, the DISM /ScanHealth returns the following errors:
- DISM Error 1726 – “The remote procedure call failed”;
- DISM Error 1910 – “The object exporter specified was not found”.
It definitely means that your Windows image is corrupted and needs to be repaired.
Repair Windows Image Using DISM /RestoreHealth
To fix corruption in the Windows image Component Store, you must use the RestoreHealth option of the DISM command. This option will allow you to fix errors found in the Windows image, automatically download and replace files of damaged or missing components with original versions of files from Windows Update (your computer must have direct Internet access). Run the command:
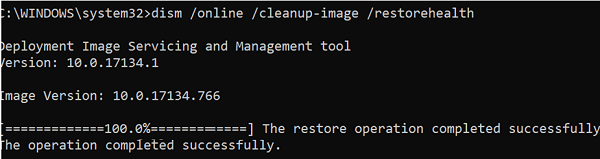
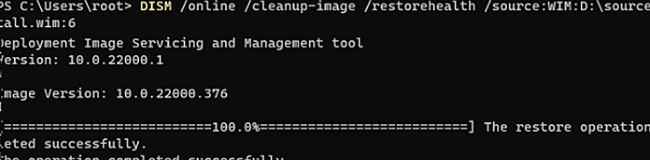
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth The process of scanning and repairing the Component Store may take quite a long time (30 minutes or more). DISM will automatically download and replace the files of corrupted or missing components with original file versions from Windows Update servers.
If the repair has been successful, the following message will appear:
The restore operation completed successfully.
DISM /RestoreHealth: The Source Files Could Not Be Found
If your computer (server) has no direct Internet access (located behind a proxy, or have used internal WSUS to get security and build updates) or Windows Update service is disabled/damaged (how to repair Windows Update client), then the following errors appear when repairing the Component Store:
- 0x800f0906 – The source files could not be downloaded. Use the source option to specify the location of the files that are required to restore the feature;
- 0x800f0950 – DISM failed. No operation was performed;
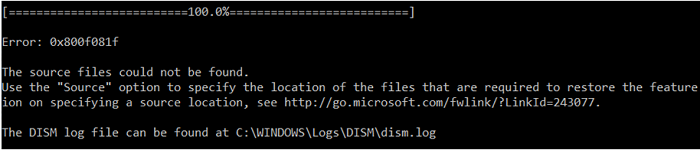
- 0x800F081F – The source files could not be found. Use the “Source” option to specify the location of the files that are required to restore the feature.
In all of these cases, you can use alternative ways to get the source Component Store files. It can be:
- Installation disk/USB flash drive/ISO image;
- Mounted wim/esd file;
- Folder \sources\SxS from the installation disk;
- The install.wim (esd) file with the Windows installation image.
You can specify a WIM or an ESD file with the original Windows installation image to be used as a source to repair the system files. Suppose, you have mounted an installation Windows 11 ISO to the virtual drive D:.
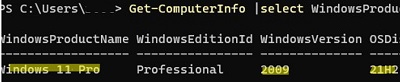
Check which version of Windows is installed on your computer using the following PowerShell command:
Get-ComputerInfo |select WindowsProductName,WindowsEditionId,WindowsVersion, OSDisplayVersion
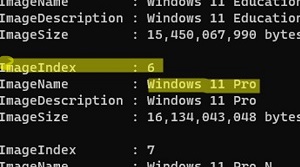
List the available Windows editions in the installation wim image:
Get-WindowsImage -ImagePath "D:\sources\install.wim"
In our case, the Windows 11 Pro image in the install.wim file has ImageIndex = 6.
To repair the Component Store from a local WIM/ESD file using the local source files (without using Windows Update online services), run the following command (remember to specify the Windows version index in the image file):
DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth /source:WIM:D:\sources\install.wim:6 /limitaccess
or:
DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth /source:ESD:D:\sources\install.esd:6 /limitaccess
- Error: 50: DISM does not support servicing Windows PE with the /Online option – this means your DISM thinks you are using a WinPE image. To fix this, remove the registry key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\MiniNT; - DISM Error 87: make sure the DISM command is written correctly, make sure you are using the DISM version for your Windows version (usually when booting in WinPE/ WinRE).
You can find the DISM log of scanning and repair of the system files here: C:\Windows\Logs\CBS.log.
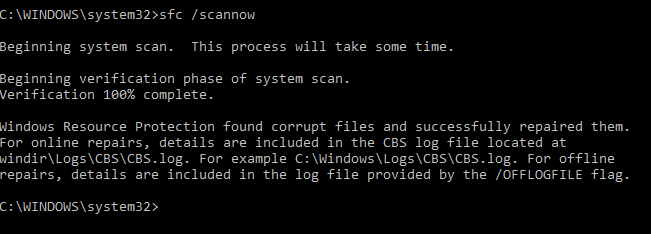
After the component store has been repaired, you can run the system file checker tool (sfc /scannow). It is likely that it will be able to restore the damaged or missing system files (Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files and successfully repaired them).
If the SFC.exe doesn’t detect any damage to the system files, a message will appear
Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations.
Repair-WindowsImage: Repairing Windows Image Component Store with PowerShell
The version of PowerShell in Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2016/2019/2022 has a cmdlet similar to the DISM commands discussed above. To scan the Windows component store and find any corruptions, run this command:
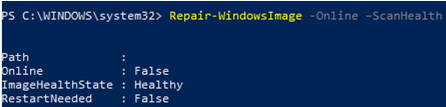
Repair-WindowsImage -Online –ScanHealth
If no errors are found in the Component Store, the following message appears:
ImageHealth State: Healthy
To repair Windows Component Store files, run:
Repair-WindowsImage -Online -RestoreHealth
If you don’t have direct Internet access, this command may hang during the image repairing process. You can restore the system components from the local Windows image file (install.wim/install.esd) copied from the Windows 10 installation ISO image. Here you also need to specify the Windows version index in the wim file as the recovery source:
Repair-WindowsImage -Online -RestoreHealth -Source F:\sources\install.wim:5 -LimitAccess
Use DISM Offline to Repair Windows Image
If Windows doesn’t boot correctly, you can use DISM to check and repair system files of your Windows image offline.
- Boot your device from the Windows installation image (you can use the Media Creation Tool to create a bootable Windows USB stick) and press
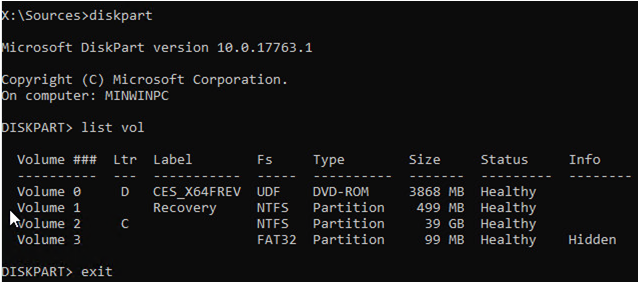
Shift + F10on the initial Windows install screen; - To check the drive letters assigned in WinPE, run the command
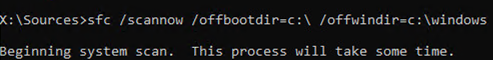
diskpart->list vol(in my example, the drive letter C:\ is assigned to the disk, on which Windows is installed, and I will use it in the next commands); - Check the system files and repair the corrupted ones with the command:
sfc /scannow /offbootdir=C:\ /offwindir=C:\Windows
- To repair the offline Windows image, use the following command (I am using a WIM file with the Windows 10 installation image from which the computer is booted as a source to restore my offline Windows image):
Dism /image:C:\ /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:D:\sources\install.wim
- If there is not enough free space on the target disk, you will need a separate drive, e. g., F:\, on which you will create an empty folder
mkdir F:\scratch. Perform a repair of the component store using the scratch dir with the command:Dism /image:C:\ /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:D:\sources\install.wim /ScratchDir:F:\scratch
DISM /Add-Package–install MSU/CAB update files, integrate security updates into your Windows image;DISM /Get-Drivers– get the list of installed drivers;DISM /Add-Driver– inject drivers to Windows installation image;DISM /Add-Capability– installing additional Windows features via Features on Demand (FoD). For example, RSAT, OpenSSH server, or Windows SSH client);DISM /Enable-Featuresand/Disable-Features– enabling and disabling Windows components (for example, the SMBv1 protocol);Dism.exe /StartComponentCleanup– cleanup the Component Store and remove old component versions (from the WinSxS folder);Dism /set-edition– upgrading from the evaluation to full Windows version without reinstalling.


5 comments
Wow thank a lot. Can it solve the “missing Winre” to create a recovery drive?
Good article. Thank you so much!
I need to do an offline DISM repair of my Windows 10 but the boot usb disk created does not have an install.wim file. Instead, it has install.esd file. As mentioned in the online DISM repair I used it in the /Source parameter (/Source:D:\sources\install.esd) . But during the DISM repair I get error saying source not found. The log file has many entries mentioning failure… the first failure log says –
DISM DISM Provider Store: PID=1396 TID=1740 Failed to get and initialize the PE Provider. Continuing by assuming that it is not a WinPE image. – CDISMProviderStore::Final_OnConnect
Further the log file also has these entries :
CBS Session: 376_1129843 initialized by client DISM Package Manager Provider, external staging directory: (null), external registry directory: (null)
CBS Exec: Addsource called, Session: 376_1129843, Client: DISM Package Manager Provider, from GPO: No, Path: E:\Sources\install.esd
CBS The alternate source path directory could not be accessed [HRESULT = 0x8007007b – ERROR_INVALID_NAME]
Can you please help me understanding why it could be failing? And how to resolve it?
Appreciate your help
Edit : The actual value for /Source I used is /Source:E:\sources\install.esd and not /Source:D:\sources\install.esd as I mentioned previously. (My USB boots into E drive. Windows is on C: )
I am trying to do the offline DISM repair from a USB stick created with the Windows Media Creator but there is no file “install.wim” in the X:/sources/ folder.